Diabetes
refers to a group of metabolic diseases where in the person’s Blood Glucose
(Sugar) level is high.
The
increase in Blood Glucose level can be:
- Due to inadequate insulin production.
- Or improper response of body’s cells to *insulin.
- Or Both.
Almost
close to 10% of world population has diabetes and yet there is no cure. People with diabetes need to manage their
disease to stay healthy.
*insulin
is a hormone that allows the body to use Glucose (sugar) from the food we eat
for energy or to store Glucose for future use. It helps in regulating the Blood
sugar level from getting too high or too low.
Common consequences of diabetes:
Uncontrolled
or poorly controlled diabetes puts you at risk. High Blood Sugar(Glucose) levels over a prolonged time, potentially damage your
blood vessels internally and cause the below complications.
Diabetes & Food Planning:
People
often tend to associate blood sugar level only with “table Sugar” or “sweetened
food items”. The term “Sugar” used in association with diabetes refers to “Glucose”
and not just only table sugar / sweetened food items.
To understand diabetes, certain basics of nutrition and how it
affects blood sugar level needs to be understood.
We
get energy and calories from the food we eat. Our bodies convert food into
energy.
The
food we eat can be broadly categorised into Carbohydrate, Protein and Fat. Our
main source of energy is carbohydrates; our bodies convert carbohydrates into
Glucose, a type of sugar.
Let’s
have a closer look at each of these categories of food w.r.t how they affect
blood sugar level.
The
key is to eat balanced meals with right
amounts of protein, carbohydrate and fat so that blood sugar does not rise too
high or too quickly.
Being
overweight, obese & blood cholesterol, adversely affects diabetes, hence
while planning for balanced meal, also a check
on the overall calorie intake is essential.
Few tips for food planning:
- Keep a check on overall calorie intake, by reading the food labels or by checking the same nutrition websites.
- Eat regularly to avoid severe fluctuation in blood sugar levels.
- Cut down on portion sizes.
- Avoid calorie dense food or sugary drinks. Food/beverages with added sugar or salt. Pay attention to food/nutrition labels.
- Have vegetables / fruits, nuts as healthy snacks instead of the usual calorie dense ones.
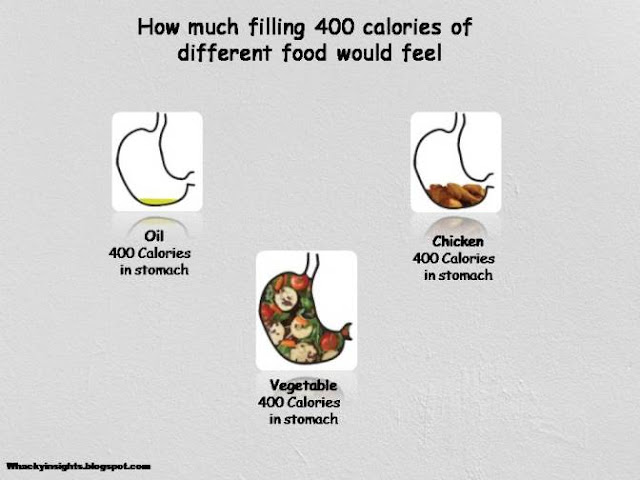
- Raw vegetables / fruits are high in fiber content, will keep you full for longer and also do not cause blood sugar hike.
- Whole Grains are high in fiber and are a healthy source of carbohydrate.
- Food with low GI values helps in better management of diabetes and also to reduce overall calorie intake. Glycemic Index (GI) is a relative ranking of carbohydrate in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates with a low GI value (55 or less) are slowly digested, absorbed and metabolised and cause a lower and slower rise in blood glucose.
- Reduce intake of saturated and trans fats for example go for grill over frying.
- Avoid partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. Limit saturated and trans fat & replace them with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
- Reduce fat intake, select skim (fat free) milk and low fat dairy products.
- Reduce consumption of cheese & butter; instead go for healthier version of sauces.
- Cut down on alcohol & smoke.
Diabetes & Exercise:
Exercise
plays a key role in preventing and controlling blood sugar hike. And it is a
proven way to help manage diabetes. Exercise / physical activity improves
insulin sensitivity by helping body’s cells to effectively utilise available
insulin.
Physical
activity also helps in regulating blood glucose levels by stimulating a
separate mechanism (independent of insulin) to allow the cells to use glucose
for energy.
30 minutes
of daily Aerobic exercise like brisk
walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, dancing etc at least 5 times weekly is recommended for adults. For those who cannot
shell out straight away 30 minutes, several shorter workouts totaling 30 mins
will prove similarly beneficial.
Strength training exercises
like lifting free weights, sit ups, squats, planks, pushups etc increase
resting metabolism of the body. Thereby helps in reducing blood sugar levels
and increases insulin sensitivity. Strength training is recommended at least
twice a week, in addition to recommended aerobic exercises.
Stretching exercises
and the like of yoga, lowers stress levels, increases flexibility, prevents
muscle aches and indirectly contribute.
Few
incidental activities which can be used to put in more physical activity are:
For
effective management of diabetes drugs & insulin treatment is not
sufficient, exercise & diets are essential and go hand in hand for better
management.
Also
keeping a check on blood pressure & cholesterol level, helps to prevent
complications.
Note : This Article may not be treated as a substitute to doctor's consultation, this is generalised information for an overall wellbeing.
Note : This Article may not be treated as a substitute to doctor's consultation, this is generalised information for an overall wellbeing.






Comments
Post a Comment